Anxiety in Elderly Individuals: What You Need to Know

Although you may not know it, you could have a loved one who is suffering from anxiety. More than twenty percent of older adults worldwide suffer from mental and neurological disorders.
That may not seem like a big number, but one in every five people could be closer to home than you think. With this in mind, it’s best to be on the safe side and learn what anxiety looks like in elderly individuals, so that you can be a comfort to your loved ones.
Don’t understand what anxiety looks like in elderly patients? Not sure how to deal with it or treat it? We’re here to help! Read our in-depth guide below to learn everything you need to know.
What Causes Anxiety in Elderly Individuals?
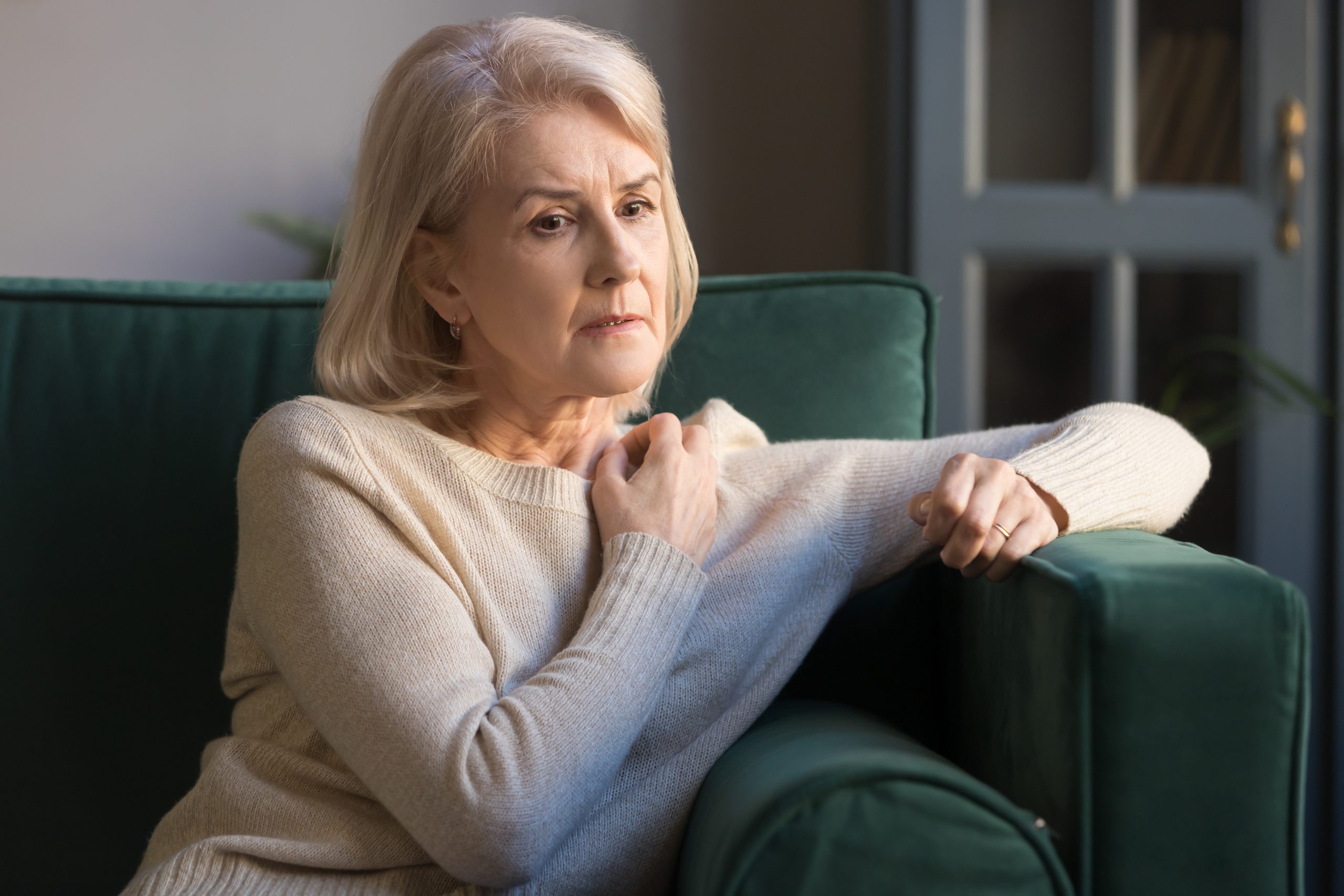

Anxiety in elderly individuals does not need a specific trigger. It can happen due to environmental factors and situational factors. Elderly individuals may feel anxious because they live alone and are unable to see their loved ones as often as they were previously accustomed to.
They can also feel guilty because they have to rely on friends and family to do their everyday tasks. The decline of their memory, concentration, and communication abilities may also lead them to overthink.
They may also fear the end of life. You should take notice of their behavior and what they say in order to understand the causes of their anxiety.
Types of Anxiety
Don’t think that anxiety looks the same in everyone. There are a variety of types of anxiety. Take note of the following types to better understand what kind of problems your loved one may be going through.
Panic Disorder
Panic disorder is characterized by constant episodes of fear and panic attacks. People may think that they are about to have a heart attack due to the spike in blood pressure during such episodes. This is one of the most common types of anxiety.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
People who suffer from generalized anxiety disorder have constant, chronic anxiety, exaggerated worry, and tension. These symptoms arise even when there is little or nothing to provoke such feelings. They may feel fine one moment but become overwhelmed by a sensation of dread the next.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Those with obsessive-compulsive disorder often have unwanted thoughts, which turn to obsessions, and repetitive behavior, or compulsions. Those with this disorder have to do compulsive actions to prevent obsessive thoughts or make them go away.
Phobias
Phobias are extreme and irrational fears of things that pose little to no threat. Phobias lead those who suffer from them to avoid certain objects or situations, which can limit their ability to engage in everyday life. Some examples of phobias are being afraid of social interaction, driving cars, thunder, and more.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder
Post-traumatic stress disorder, or PTSD, happens after experiencing a terrifying event like violence and abuse. It also happens when something or someone threatens the life or safety of the person who suffers from it. It often occurs to soldiers, but even those who have not served can experience PTSD.
Symptoms of Anxiety
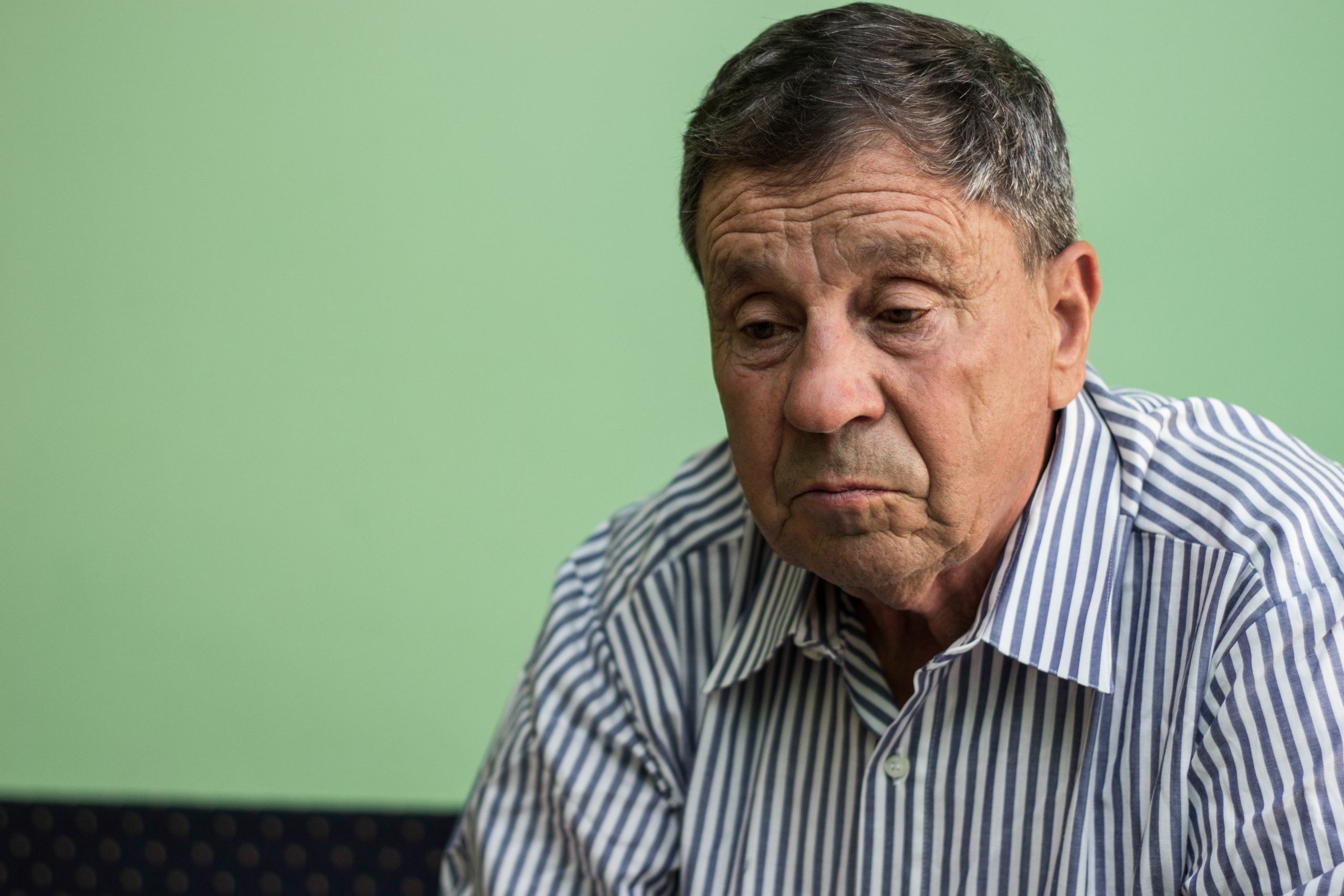

Some symptoms of anxiety in elderly individuals may not seem obvious. It’s hard to understand what can be a normal shift in mood and what warrants deeper examination. Those suffering from anxiety may experience a range of symptoms from the categories below:
Behavioral Symptoms
- Avoiding objects or situations
- Urging others to manage their responsibilities
- Avoiding eye contact
- Trouble making decisions
- Easily started
Emotional Symptoms
- Easily overwhelmed
- Worried about physical symptoms
- Fear of certain situations, objects, and events
- Always tense and nervous
- Uncontrollable panic attacks
Physical Symptoms
- Increased heart rate
- Constant vomiting, nausea, and pain in the stomach
- Muscle tension and pain
- Detached from their surroundings
- Insomnia
- Light-headed, dizzy, or faint
- Random numbness or tingling
- Hot or cold flashes
In most cases, only some symptoms will be present, rather than all of the above symptoms. However, if not dealt with, anxiety can escalate and cause more problems. Those suffering from anxiety can experience a weakened immune system, high blood pressure, fatigue, and more.
How Can You Help?
How can you help elderly people with anxiety? The most important step is to seek a medical professional. However, there are other steps involved, including the following.
Listen to Their Troubles
Actively listening to the troubles of elderly loved ones is as important as assuring them that everything will be alright. Let them know that it is common to feel anxiety during times of stress and transition.
Reassure them that there is nothing wrong with asking for help when they feel distressed. Your loved ones need to know that they can speak freely and be reminded that you are there to assist with their concerns.
Try Out Mindfulness
Mindfulness teaches you how to respond to stress as well as what emotions are driving you to make certain decisions.
Methods like meditation and therapy teach your elderly loved ones to manage their present situations. Even listening to music or taking a quiet bath can help manage emotions during tough times.
Plan Activities for Them
Most of the time when you spend time with your elderly loved ones, it can reduce anxiety and even depression. Spend your time reliving happy memories and do your best to avoid reminding them of negative times.
Try to cook some of their favorite recipes. It’s a great way to relive the good times when they used to teach you to cook. You can also consider watching old shows that they used to enjoy, like black and white cartoons.
Ease Anxiety in Older Adults
Be a part of the solution and help lessen the anxiety in elderly individuals. Don’t allow their problems to continue unassisted. Stay by their side and don’t let them go through this alone.
You don’t have to do this either. Feel free to contact us for any questions regarding how we can help you with transitional medicine, senior placement, home care, and consulting.